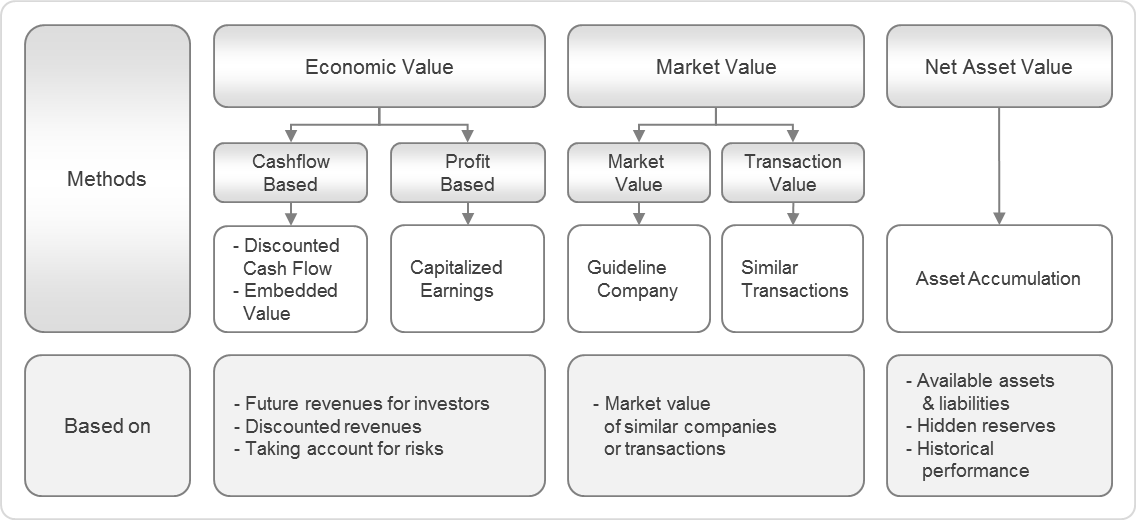
Although the list above consists of examples of fixed assets, they aren’t necessarily universal to all companies. In other words, what is a fixed asset to one company may not be considered a fixed asset to another. If the car is being used in a company’s operations to generate income, such as a delivery vehicle, it may be considered a fixed asset.
Index Providers: Whales Behind the Scenes of ETFs – The Harvard Law School Forum on Corporate Governance
Index Providers: Whales Behind the Scenes of ETFs.
Posted: Tue, 08 Aug 2023 13:32:14 GMT [source]
They are not sold to customers or held for investment purposes. As such, companies are able to depreciate the value of these assets to account for natural wear and tear. Fixed assets most commonly appear on the balance sheet as property, plant, and equipment (PP&E). Fixed assets are often referred to as property, plant, and equipment, or PPE—the three most common kinds of fixed assets. For example, the fixed assets of a frozen cookie dough manufacturer might include a corporate office (property), a cookie dough factory (plant), and machines that make cookie dough (equipment).
They support the business.
Fixed assets are subject to depreciation, which accounts for their loss in value over time, whereas intangible assets are amortized. Fixed assets are often contrasted with current assets, which are expected to be converted to cash or used within a year. Fixed assets are physical or tangible items that a company owns and uses in its business operations to provide services and goods to its customers and help drive income. These assets, which are often equipment or property, provide the owner long-term financial benefits. It is expected that a business will keep and use fixed assets for a minimum of one year. The value of fixed assets decline as they are used and age (except for land), so they can be depreciated.
Fixed assets are company-owned, long-term tangible assets, such as forms of property or equipment. These assets make up its day-to-day operations to generate income. Being fixed means they can’t be consumed or converted into cash within a year. As such, they are subject to depreciation and are considered illiquid. Contrary to a noncurrent, fixed asset, a current asset is an asset that will be used or sold within one year.
Additionally, buying rock salt to melt ice in the parking lot would be considered an expense and not an asset at all. Fixed tangible assets are depreciated over their lifetimes to reflect their use and the depletion of their value. Depreciation reduces the recorded cost of the asset on the company balance sheet.
Fixed Assets Defined: Benefits & Examples
For completeness, non-current assets are also reduced in value over their useful life. As non-current assets are intangible, the process is known as amortisation. Current assets are not subject to depreciation or amortisation because they are expected to be used within a year. For example, a company that purchases a printer for $1,000 with a useful life of 10 years and a $0 residual value would record a depreciation of $100 on its income statement annually. Information about a corporation’s assets helps create accurate financial reporting, business valuations, and thorough financial analysis. Investors and creditors use these reports to determine a company’s financial health and decide whether to buy shares in or lend money to the business.

On average, most businesses have a turnover rate between 5 and 10. A higher turnover rate means greater success in its ability to manage fixed-asset investments. There is give two examples of fixed assets no specific ratio or range that defines a “good” turnover ratio. Instead, companies’ turnover ratios are very industry specific and other factors must be considered.
Income statements.
They are also expected to retain their value or even increase in value. It is, however, fairly unusual for businesses to have these assets. ● Machinery – This can include any type of machinery that is used by your business, such as manufacturing equipment or office machines.

At the end of their lifecycle, fixed assets are often converted into cash. Simply put, a fixed asset is an item of value owned by a business that has a physical form. The most common examples of fixed assets include buildings, vehicles, and machinery.
Capitalizing means that the item is recorded as a long-term asset, rather than an expense. According to generally accepted accounting principles, known as GAAP, in order for an item to be capitalized, it must be owned by the business and have a useful life of more than one year. Current assets include rotating physical goods, such as supplies and inventory. Fixed assets are tangible items a business owns that are held on a long-term basis.
How can financial institutions blend digital and human successfully
Here’s what fixed assets mean and why they matter for small business owners. Assets are something acquired by an organization to generate revenues. Modern rules of accounting are followed for recording assets in the books of accounts of an organization.
Asure Announces Second Quarter 2023 Results News bakersfield … – The Bakersfield Californian
Asure Announces Second Quarter 2023 Results News bakersfield ….
Posted: Mon, 07 Aug 2023 20:09:15 GMT [source]
These items are typically used by businesses to generate revenue or create jobs. When a company purchases a fixed asset, they record the cost as an asset on the balance sheet instead of expensing it onto the income statement. A fixed asset shows up as property, plant, and equipment (a non-current asset) on a company’s balance sheet.
Presumably, the business will own and use those items for many years, so they are listed as fixed assets on the balance sheet. Additionally, fixed assets are used by financial experts to determine the value or profits of a company. Financial experts need to determine whether a company is profitable, and fixed assets are one aspect that can help them decide.
- In this case, the laptop would be recorded on the company’s balance sheet as property, plant, and equipment (PP&E).
- Fixed tangible assets are depreciated over their lifetimes to reflect their use and the depletion of their value.
- For example, the fixed asset turnover ratio is used to determine the efficiency of fixed assets in generating sales.
- LiveFlow can help businesses track and manage their assets with ease.
- The term fixed asset refers to a long-term tangible piece of property or equipment that a firm owns and uses in its operations to generate income.
For instance, if you sold your building, it would take weeks or months to find a buyer, have their financing and paperwork processed, and close on the sale. Additionally, fixed assets have a significant impact on the business. They often take a sizable investment to acquire and are intended to be used over a long period of time.
A fixed asset, or noncurrent asset, typically is an actual, physical item that a company buys and uses to make products or servicea that it then sells to generate revenue. For example, machinery, a building, or a truck that’s involved in a company’s operations would be considered a fixed asset. Fixed assets are long-term assets, meaning they have a useful life beyond one year. While tangible assets are the main type of fixed asset, intangible assets can also be fixed assets.
- The major difference between the two is that fixed assets are depreciated, while current assets are not.
- ● Land – This is the property on which your business is located.
- These experts collect the assets’ information and their depreciation rate and establish their reports using them.
- The company projects that it will use the building, machinery, and equipment for the next five years.
For example, if you own a factory thanks to financing from the bank, your fixed asset liability is the money you still owe on the mortgage. Note that one company’s fixed asset might not count as a fixed asset for another company. For instance, a cybersecurity company might list computer equipment as a fixed asset. In contrast, an office supply business that sells computers wouldn’t, because the computer equipment, in this case, is the merchandise. Fixed assets are essential to the operation of virtually every kind of business—if you’re running a small-to-midsize business, you probably have at least one fixed asset.